http高并发服务器实现
基础知识
html,全称为html markup language,超文本标记语言。
http,全称hyper text transfer protocol,超文本传输协议。用于从万维网(WWW:World Wide Web)服务器传输超文本到本地浏览器的传送协议。
客户端请求的格式:
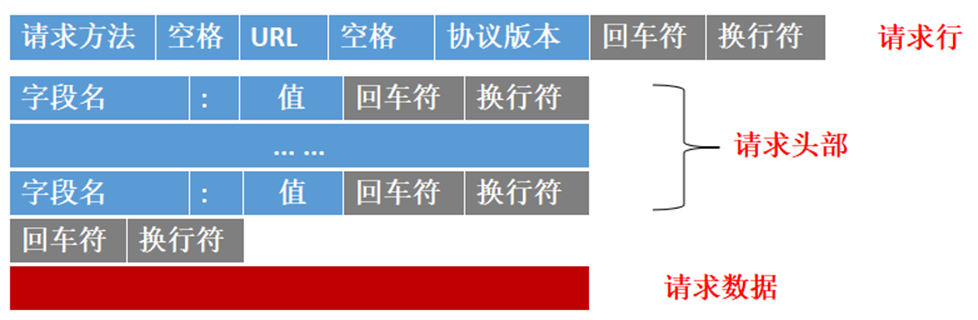
请求方法有:GET、POST等。URL:请求地址。协议版本:HTTP的版本。
服务器响应的格式:
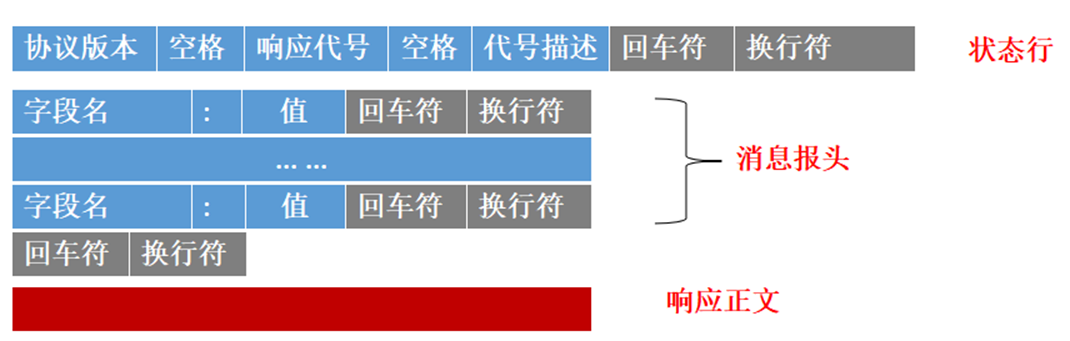
| ----- | 响应代号 | 代号描述 |
|---|---|---|
| 服务器上存在请求的内容,并可以响应给客户端 | 200 | OK |
| 客户端的请求有异常,方法有问题 | 501 | Method Not Implemented |
| 服务器收到请求后,因为自生的问题没法响应 | 500 | Internal Server Error |
| 请求的内容不存在 | 404 | NOT FOUND |
| 客户端发送的请求格式有问题等(一般不存在) | 400 | BAD REQUEST |
http服务器实现
文件概念
文件的Inode元信息表示文件的索引节点,存储着文件的元信息,例如文件得创建者,文件创建日期,文件大小等。每个inode都有一个号码,操作系统用inode号码来识别不同的文件,使用命令ls -i可以查看inode号码。
stat函数
stat是C++用于读取文件资源管理器的库函数,头文件为:
#include<sys/stat.h> #include<sys/types.h> #include<unisted.h> int stat(const char *path,struct stat *buf); int fstat(int fd,struct stat *buf); int lstat(const char *path,struct stat *buf); parameter: path:文件路径 buf:传入的保存文件状态的指针,用于保存文件的状态 fd:文件描述符 return:成功返回0,失败返回-1,并设置errno
stat的结构体内容如下所示:
struct stat {
dev_t st_dev; /* ID of device containing file */
ino_t st_ino; /* inode number */
mode_t st_mode; /* S_ISREG(st_mode) 是一个普通文件 S_ISDIR(st_mode) 是一个目录*/
nlink_t st_nlink; /* number of hard links */
uid_t st_uid; /* user ID of owner */
gid_t st_gid; /* group ID of owner */
dev_t st_rdev; /* device ID (if special file) */
off_t st_size; /* total size, in bytes */
blksize_t st_blksize; /* blocksize for filesystem I/O */
blkcnt_t st_blocks; /* number of 512B blocks allocated */
time_t st_atime; /* time of last access */
time_t st_mtime; /* time of last modification */
time_t st_ctime; /* time of last status change */
};并发和并行
并发与并行的区别简单来说所谓的并发指的是多个进程按照一定的时间间隔进行,只不过这个时间间隔很小,人类难以感受到而已,实际上在微观角度,进程的并发执行还是顺序执行。
高并发:高并发是互联网分布式框架设计中必须要考虑的因素之一,通常指的是,通过设计系统能够同时并行处理很多请求。
线程可以并行的执行任务
//头文件 #include<pthread.h> //函数 int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread,const pthread_attr_t *attr,void *(*start_routine)(void *),void *arg); pthread_t:当前Linux中可理解为:typedef unsigned long int pthread_t args1:传出参数,保存系统为我们分配好的线程ID; args2:通常传NULL,表示使用线程默认属性。若想使用具体属性也可以修改该参数。 args3:函数指针,指向线程主函数(线程体),函数运行结束,则线程结束。 args4:线程主函数执行期间所需要使用的函数。
在一个线程中调用pthread_create()创建新的线程后,当前线程从pthread_create()返回继续往下执行,而新的线程所执行的代码由我们传给pthread_create的函数指针start_routine决定。start_routine函数接收一个参数,是通过pthread_create的arg参数传递给它的,该参数的类型为void *,这个指针按什么类型解释由调用者自己定义。start_routine的返回值类型也是void *,这个指针的含义同样由调用者自己定义。start_routine返回时,这个线程就退出了,其它线程可以调用pthread_join得到start_routine的返回值。
pthread_create成功返回后,新创建的线程的id被填写到thread参数所指向的内存单元。
attr参数表示线程属性。
pthread_exit (status)
pthread_exit用于显式地退出一个线程。通常情况下,pthread_exit() 函数是在线程完成工作后无需继续存在时被调用。
如果 main() 是在它所创建的线程之前结束,并通过 pthread_exit() 退出,那么其他线程将继续执行。否则,它们将在 main() 结束时自动被终止。
gcc/g++ 编译时需要添加 -pthread进行编译。
gcc test.c -pthread -o test
简单的多线程实例:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <pthread.h>
using namespace std;
#define NUM_THREADS 5
void *PrintHello(void *threadid)
{
// 对传入的参数进行强制类型转换,由无类型指针变为整形数指针,然后再读取
int tid = *((int*)threadid);
cout << "Hello Runoob! 线程 ID, " << tid << endl;
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
int main ()
{
pthread_t threads[NUM_THREADS];
int indexes[NUM_THREADS];// 用数组来保存i的值
int rc;
int i;
for( i=0; i < NUM_THREADS; i++ ){
cout << "main() : 创建线程, " << i << endl;
indexes[i] = i; //先保存i的值
// 传入的时候必须强制转换为void* 类型,即无类型指针
rc = pthread_create(&threads[i], NULL,
PrintHello, (void *)&(indexes[i]));
if (rc){
cout << "Error:无法创建线程," << rc << endl;
exit(-1);
}
}
pthread_exit(NULL);
}最终代码
服务器代码样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <ctype.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#define SERVER_PORT 80
void do_http_request(int client_sock);
int get_line(int client_sock, char *buf, int size);
void do_http_response(int client_sock, const char *path);
void headers(int client_sock, FILE *resource);
void cat(int client_sock, FILE *resource);
void not_found(int client_sock);
void inner_error(int client_sock);
int main(void)
{
int sock;
struct sockaddr_in server_addr;
sock = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
// printf("wait \n");
bzero(&server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
server_addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
server_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(INADDR_ANY);
server_addr.sin_port = htons(SERVER_PORT);
bind(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&server_addr, sizeof(server_addr));
listen(sock, 128);
printf("wait client connect\n");
int done = 1;
while (done)
{
struct sockaddr_in client;
int client_sock, len, i;
char client_ip[64];
char buf[256];
socklen_t client_addr_len;
client_addr_len = sizeof(client);
client_sock = accept(sock, (struct sockaddr *)&client, &client_addr_len);
printf("client ip: %s \t port is : %d \n", inet_ntop(AF_INET, &client.sin_addr.s_addr, client_ip, sizeof(client_ip)), ntohs(client.sin_port));
pthread_t tid;
int* ptr_int=NULL;
int err=0;
ptr_int=(int*)malloc(sizeof(int));
*ptr_int=client_sock;
if(err=pthread_create(&tid,NULL,do_http_request,(void*)ptr_int)){
printf(stderr,"cannot create thread. reason: %s\n",strerror(errno));
if(ptr_int) free(ptr_int);
}
// do_http_request(client_sock);
// close(client_sock);
}
close(sock);
return 0;
}
void* do_http_request(void* p_client_sock)
{
int len = 0;
char buf[256], method[64], url[256], path[256];
int client_sock=*(int *)p_client_sock;
struct stat st;
// http response struct: request_method url protocol_version \r\n
len = get_line(client_sock, buf, sizeof(buf));
if (len > 0)
{
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (!isspace(buf[j]) && i < sizeof(method) - 1)
{
method[i] = buf[j];
i++;
j++;
}
// set end tag
method[i] = '\0';
printf("method: %s\n", method);
// method is GET request
if (strncasecmp(method, "GET", i) == 0)
{
printf("request method is GET\n");
while (isspace(buf[j]))
{
j++;
}
i = 0;
while (!isspace(buf[j]) && i < sizeof(url) - 1)
{
url[i] = buf[j];
i++;
j++;
}
url[i] = '\0';
if (strncasecmp(url, "/favicon.ico", i) == 0)
{
strcpy(url, "/hello.html");
}
printf("url:%s\n", url);
// read surplus request
do
{
len = get_line(client_sock, buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("%s\n", buf);
} while (len > 0);
// get local url file, and process ? in url, eg. url=128.0.0.2/hel.html?wang=dedefe
char *pos = strchr(url, '?');
if (pos)
{
// \0 represent string end tag
*pos = '\0';
printf("real url: %s\n", url);
}
sprintf(path, "./html_doc%s", url);
printf("path:%s\n", path);
// execute http response
// if file is exist, to response 200, ok,and send html file,else response 404 NOT FOUND
if (stat(path, &st) == -1)
{
printf("--------------------");
fprintf(stderr, "stat %s failed. reason :%s\n", strerror(errno));
not_found(client_sock);
}
else
{
printf("*****************");
if (S_ISDIR(st.st_mode))
{
strcat(path, "/index.html");
}
do_http_response(client_sock, path);
}
}
else
{
// request method is not GET,read http head, and response client request
fprintf(stderr, "warning, other request [%s]\n", method);
do
{
len = get_line(client_sock, buf, sizeof(buf));
printf("%s\n", buf);
} while (len > 0);
// unimplement()
}
}
else
{
printf("method is error");
}
close(client_sock);
if(p_client_sock) free(p_client_sock);
}
void do_http_response(int client_sock, const char *path)
{
FILE *resource = NULL;
resource = fopen(path, "r");
if (resource == NULL)
{
not_found(client_sock);
return;
}
// send http head
headers(client_sock, resource);
// send http body
cat(client_sock, resource);
// printf("end response!!!!");
fclose(resource);
}
void headers(int client_sock, FILE *resource)
{
struct stat st;
int fileid = 0;
char temp[64];
char buf[1024] = {0};
strcpy(buf, "HTTP/1.0 200 OK\r\n");
strcat(buf, "Server: Martin Server\r\n");
strcat(buf, "Content-Type: text/html\r\n");
strcat(buf, "Connection: Close\r\n");
fileid = fileno(resource);
/* fstat: Get file attributes for the file, device, pipe, or socket
that file descriptor FD is open on and put them in BUF. */
if (fstat(fileid, &st) == -1)
{
inner_error(client_sock);
}
snprintf(temp, 64, "Content-Length:%d\r\n\r\n", st.st_size);
strcat(buf, temp);
printf(stdout, "header: %s", buf);
if (send(client_sock, buf, strlen(buf), 0) < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "send fail,data %s, reason %s", buf, strerror(errno));
}
}
void cat(int client_sock, FILE *resource)
{
char buf[1024];
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), resource);
while (!feof(resource))
{
int len = write(client_sock, buf, strlen(buf));
if (len < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "send boady error. reason %s\n", strerror(errno));
break;
}
fprintf(stdout, "%s", buf);
fgets(buf, sizeof(buf), resource);
}
}
int get_line(int client_sock, char *buf, int size)
{
int count = 0;
char ch = '\0';
int len = 0;
while (count < size - 1 && ch != '\n')
{
len = read(client_sock, &ch, 1);
if (len == 1)
{
if (ch == '\r')
continue;
else if (ch == '\n')
break;
buf[count] = ch;
count++;
}
else if (len == -1)
{
perror("read fail");
count = -1;
break;
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "client close.\n");
count = -1;
break;
}
}
if (count >= 0)
buf[count] = '\0';
return count;
}
void not_found(int client_sock)
{
const char *reply = "HTTP/1.0 404 NOT FOUND\r\n\
Content-Type: text/html\r\n\
\r\n\
<HTML lang=\"zh-CN\">\r\n\
<meta content=\"text/html; charset=utf-8\" http-equiv=\"Content-Type\">\r\n\
<HEAD>\r\n\
<TITLE>NOT FOUND</TITLE>\r\n\
</HEAD>\r\n\
<BODY>\r\n\
<P>文件不存在!\r\n\
<P>The server could not fulfill your request because the resource specified is unavailable or none xistent.\r\n\
</BODY>\r\n\
</HTML>";
int len = write(client_sock, reply, strlen(reply));
fprintf(stdout, reply);
if (len < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "send reply failed. reason: %s\n", strerror(errno));
}
}
void inner_error(int client_sock)
{
const char *reply = "HTTP/1.0 500 Internal Sever Error\r\n\
Content-Type: text/html\r\n\
\r\n\
<HTML lang=\"zh-CN\">\r\n\
<meta content=\"text/html; charset=utf-8\" http-equiv=\"Content-Type\">\r\n\
<HEAD>\r\n\
<TITLE>Inner Error</TITLE>\r\n\
</HEAD>\r\n\
<BODY>\r\n\
<P>服务器内部出错.\r\n\
</BODY>\r\n\
</HTML>";
int len = write(client_sock, reply, strlen(reply));
fprintf(stdout, reply);
if (len <= 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "send reply failed. reason: %s\n", strerror(errno));
}
}客户端代码样例:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#define SERVER_PORT 666
#define SERVER_IP "127.0.0.1"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int sockfd;
char *message;
struct sockaddr_in servaddr;
int n;
char buf[64];
if (argc != 2)
{
fputs("Usage: ./echo_client message \n", stderr);
exit(1);
}
message = argv[1];
printf("message: %s\n", message);
sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
// 重置结构体的内存空间
memset(&servaddr, '\0', sizeof(struct sockaddr_in));
servaddr.sin_family = AF_INET;
inet_pton(AF_INET, SERVER_IP, &servaddr.sin_addr);
servaddr.sin_port = htons(SERVER_PORT);
connect(sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&servaddr, sizeof(servaddr));
write(sockfd, message, strlen(message));
n = read(sockfd, buf, sizeof(buf) - 1);
if (n > 0)
{
buf[n] = '\0';
printf("receive: %s\n", buf);
}
else
{
perror("error!!!");
}
printf("finished.\n");
close(sockfd);
return 0;
}